–
–
Technology:
Core Technology: WPU
GPROPEL utilizes a groundbreaking unique technology called Wireless Power Utilization (WPU), which powers vehicles in real-time (“use as you go”) as they move. This eliminates the need for energy storage or conversion systems, such as batteries in EVs or engines in ICE vehicles. By reducing the dead weight associated with these components, GPROPEL offers a revolutionary opportunity to enhance energy efficiency in propulsion.

Strategic Objective: GPROPEL aims to provide a transportation solution that prioritizes a more conventional speed to a very high speed suitable for urban mobility.
Speed Range: The maximum speed of the solution should fall within a range situated between the rapid transit speeds of Maglev technology (500 km/h) and the standard speeds of conventional motorways (100 km/h).
Infrastructure Utilization: GPROPEL intends to leverage existing urban infrastructure and vehicles, thereby minimizing the necessity for new construction.
Problem – Current Scenario:
IC Engines
- High Emissions: IC engines produce significant pollutants like CO2 and NOx, contributing to air pollution, climate change, and health problems.
- Fuel Dependency: They rely on fossil fuels, leading to high operational costs, exposure to volatile fuel prices, and resource depletion.
- Low Efficiency: A large portion of energy in IC engines is wasted as heat, making them less efficient compared to newer technologies.
- Frequent Maintenance: With many moving parts, IC engines require regular maintenance, increasing the overall cost and downtime.
- Regulatory Challenges: Stricter global emissions standards are making it increasingly difficult and costly to produce compliant IC engines.
EV Vehicles:

- Battery Weight and Range: Electric vehicles (EVs) require heavy batteries, which limit range and efficiency, and reduce the vehicle’s overall performance.
- Long Charging Times: Charging an EV takes significantly longer than refueling a conventional car, causing inconvenience and making long trips challenging.
- Limited Charging Infrastructure: Charging stations are not as widely available as gas stations, particularly in rural areas, limiting the practicality of EVs for many users.
- Battery Degradation: Over time, EV batteries degrade, leading to reduced range and efficiency, and requiring expensive replacements.
- Environmental Impact of Battery Production: The production and disposal of lithium-ion batteries involve significant environmental costs, including mining for raw materials and managing battery waste.
Solution:
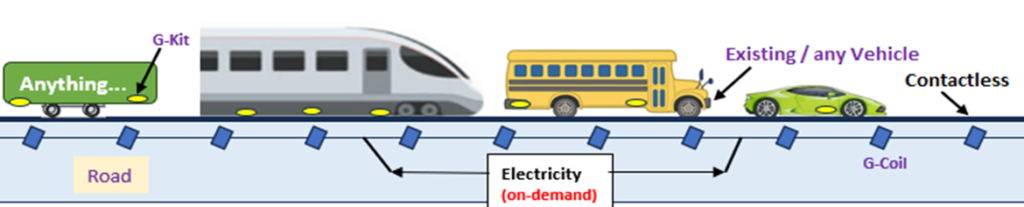
G-Road Technology: WPU (Wireless Power Utilization)
- A road infrastructure that can propel vehicles without the need for fuel or batteries.
- Energy for propulsion is sourced directly from the road’s power grid, eliminating the need for physical contact or energy storage on the vehicle.
- Existing vehicles require minimal modifications with an add-on kit to utilize this technology.
- The technology ensures zero pollution on these “G-Roads” as vehicles utilize energy from the power grid via the road rather than internal combustion engines or EV batteries.
Future Option: Redesign the Commuting
- Current commuting options such as trains and buses may be redesigned into smaller units carrying 2–6 passengers, like a car.
- These cars operate on an on-demand basis, at stations, where passengers can request transportation by pressing a button or mobile app.
- The flexibility of smaller cars allows for more efficient transportation during both peak and non-peak hours.
GPROPEL – Underground Power
Terminology and Technology Brief:
Overview:
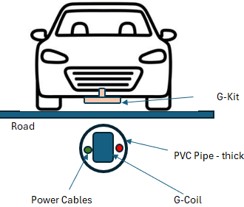
- G-Road: A special type of road equipped with technology that propels vehicles without the need for fuel or batteries. Energy is sourced indirectly from the power grid via G-Coil.
- G-Kit: An attachment or modification required for existing vehicles to utilize G-Roads. Electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers can integrate this kit into their vehicles, reducing costs as existing EVs only require approximately $200 worth of modifications.
- G-Car: A new type of car designed for use in G-Zones. G-Cars come with an in-built G-Kit and have a battery range of 50km. These cars are priced significantly lower, or almost equal to half the current price of conventional vehicles, making them more affordable for urban commuters.
- G-Zone: An urban area where all roads are built as G-Roads, ensuring near-zero pollution from vehicle emissions.
- Technology shall be demonstrated face-to-face
–

GPROPEL – Underground unique Propel Technology
–
Technology Overview
At GPROPEL, we are committed to revolutionizing transportation with our innovative system that powers vehicles directly from road infrastructure.
Wireless Power Utilization (WPU): GPROPEL leverages an innovative technology that directly powers vehicles wirelessly as they move, eliminating the need for energy storage or conversion systems.
Energy-Efficient Propulsion: By removing heavy components like batteries (in EVs) and engines (in ICE vehicles), GPROPEL significantly reduces dead weight, enabling more efficient energy use in propulsion.
On-Demand Energy Use: Energy is seamlessly supplied in real-time, enhancing operational efficiency and eliminating the inefficiencies associated with traditional energy storage and transfer systems.
G-Roads: Roads that power your vehicle, directly from the grid—No fuel, no batteries, just movement.
G-Kit: The simple, affordable attachment that turns any vehicle into a GPROPEL vehicle.
G-Car: The next generation of vehicles—clean, cheap, and perfectly designed for G-Roads.
On-demand
Underground live Electric Power
Sustainability – The Core of GPROPEL:
Zero Emissions: GPROPEL eliminates the need for fossil fuels and batteries, drastically reducing carbon emissions and air pollution.
Direct Renewable Energy: Vehicles are powered directly from renewable energy sources embedded in the roads, bypassing the need for energy storage and transitions.
Reduced Resource Consumption: By eliminating heavy batteries and fuel-based engines, GPROPEL reduces the reliance on non-renewable materials and rare earth metals used in EV battery production.
Energy Efficiency: GPROPEL’s system improves overall energy efficiency by delivering energy directly to vehicles, minimizing energy losses from storage and conversion.
Scalable Sustainable Infrastructure: GPROPEL offers a cost-effective and scalable solution that can be implemented in urban and rural areas, supporting long-term, sustainable transportation networks worldwide.
Safety first:
Propelling your car, protecting pedestrians.
No overhead live cables – rain proof, no disruption
All empty cars without or inactive fuel or batteries. No breakdown in street due to engine breakdown
Drive safe, drive green, with GPROPEL’s zero-emission roads.
Recent Developments
A miniature prototype has been developed, and preliminary simulations have been conducted.
GPROPEL aims to exceed 200 kph,
depending on infrastructure capabilities.
Global reach:
On the road to global expansion—Here’s what’s next for GPROPEL.
We’re just getting started—Here’s how GPROPEL is scaling for the future.
GPROPEL’s technology is ready to roll out worldwide—Let’s power the world’s roads together.
From city streets to highways, GPROPEL is getting ready for the global stage.
PS: While our website (www.gpropel.com) and pitch deck maintain confidentiality around the full details, we would be thrilled to provide an online demonstration.
–
